What is Agentic AI? Moving Beyond Reactive Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from systems that react to predefined rules or generate content based on patterns, to a more proactive and autonomous paradigm: Agentic AI.
Unlike traditional AI models that primarily respond to direct prompts or perform specific, narrow tasks, Agentic AI systems are designed to perceive their environment, set their own goals, make decisions, plan actions, and execute them independently, all with minimal human intervention. They possess a degree of 'agency', the capacity to act purposefully and adapt to dynamic situations.
Agentic AI Framework Architecture.
Imagine a traditional generative AI like a brilliant artist who can create stunning paintings (text, images, code) when given a specific theme or style. Agentic AI, on the other hand, is like an ambitious architect who not only designs the building but also oversees its construction from start to finish, adapts to unexpected challenges on site, and ensures the final structure meets the client's vision.
Core Characteristics of Agentic AI
- Autonomy: This is the defining feature. Agentic AI systems can operate independently, making decisions and taking actions without requiring continuous human oversight for every step. They are not merely automated scripts; they assess situations and initiate actions.
- Goal-Oriented Behavior: Agentic AI is designed with broader objectives in mind. Rather than just completing a single task, it works towards achieving a larger goal, often by breaking it down into smaller, manageable sub-tasks.
- Adaptability & Proactiveness: These systems don't just follow a static set of rules. They can observe changes in their environment, learn from new data, and adjust their strategies in real-time. They can even anticipate needs or opportunities and initiate actions without explicit instructions.
- Continuous Learning: Agentic AI systems are built to learn and improve over time. Through techniques like reinforcement learning (learning from trial and error via rewards and penalties) and self-supervised learning, they refine their understanding and strategies, becoming more effective with experience.
- Self-Awareness (Emerging): Some advanced agentic AI systems are designed with a degree of self-awareness, allowing them to monitor their performance, recognize limitations or errors, and adjust their approach accordingly.
- Tool Use & Integration: A crucial aspect of agentic AI is its ability to interact with external tools, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), databases, and other software. This allows them to gather up-to-date information, execute commands in various applications, and perform tasks that extend beyond their internal processing capabilities (e.g., sending emails, running code, searching the web).
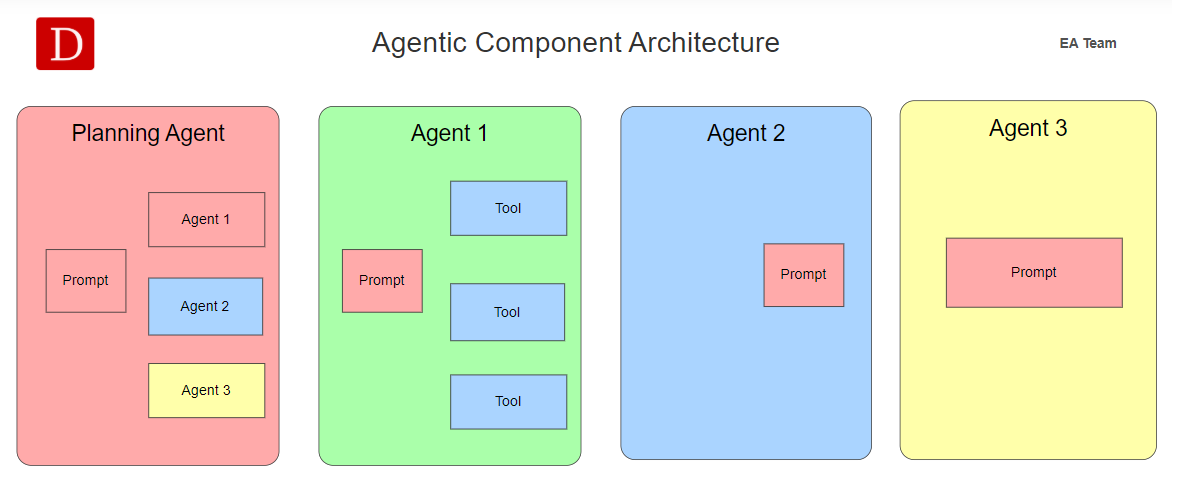
Agentic Component Architecture.
How Does Agentic AI Work? (A Simplified Architecture)
The internal workings of an Agentic AI system can be conceptualized through a modular architecture, often involving:
- Perception Module: This module is responsible for gathering and interpreting data from the environment. This could involve processing sensory data (from cameras and microphones), digital data (from databases, web pages, and APIs), or user inputs. It allows the AI to 'understand' its current state and surroundings.
- Cognitive (or Reasoning/Planning) Module: Often powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) for their advanced reasoning and understanding capabilities, this is the 'brain' of the agent. It processes perceived information, sets goals (or refines existing goals), plans sequences of actions, makes decisions, and devises strategies to achieve objectives.
- Action (or Execution) Module: This module translates the AI's decisions and plans into actual actions within the environment. This could involve sending commands to other software, interacting with physical robots, generating responses, or updating databases.
- Memory Module: Agentic AI systems maintain various forms of memory, including short-term context (what's happening now) and long-term knowledge (learned experiences, stored data, past strategies). This enables the agent to retain information over time, reflect on past performance, and make more informed decisions for the future.
- Orchestration Layer: In more complex Agentic AI systems, especially multi-agent systems, an orchestration layer coordinates and manages the interactions between different modules, tools, and even other AI agents, ensuring smooth workflow and task completion.
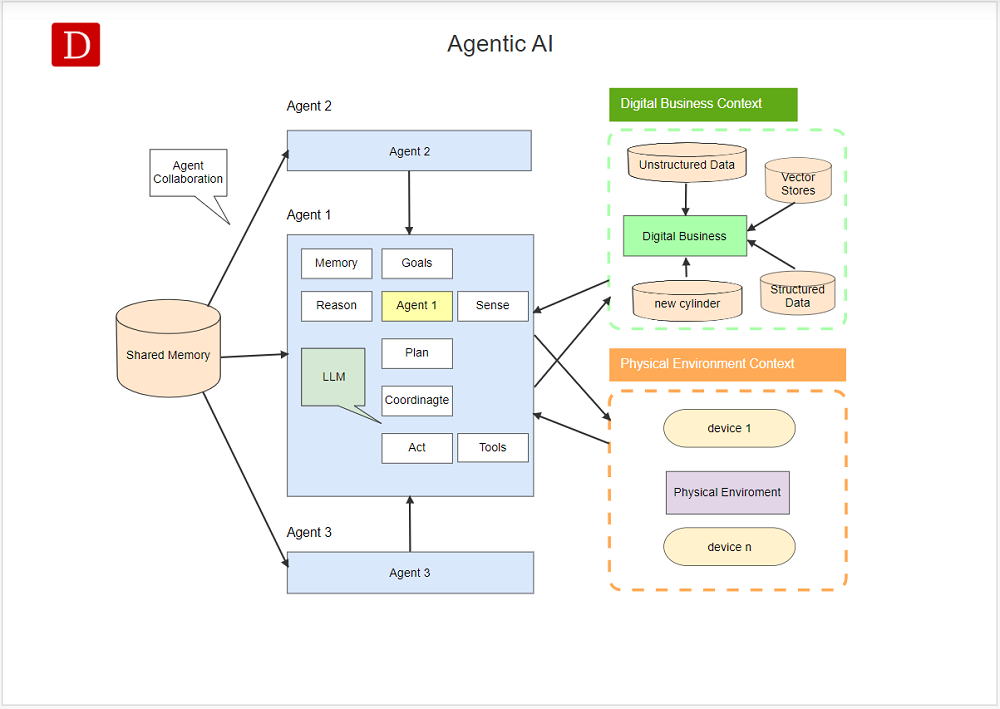
Autonomy of Agentic AI.
The Power and Promise of Agentic AI: Benefits and Real-World Applications
The shift towards Agentic AI represents a significant leap in AI capabilities, offering numerous benefits and opening up new possibilities across various industries.
Key Benefits of Agentic AI
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By automating complex, multi-step workflows that previously required significant human oversight, Agentic AI frees up human employees to focus on more strategic, creative, and complex problem-solving tasks. This leads to faster processes, reduced bottlenecks, and streamlined operations.
- Enhanced Scalability: Agentic AI systems can rapidly scale to handle increasing volumes of data and tasks without a proportional increase in human resources. This is particularly valuable for businesses experiencing growth or fluctuating demands.
- Improved Decision-Making: With the ability to gather, analyze, and learn from vast amounts of data in real-time, Agentic AI can make more accurate, consistent, and data-driven decisions faster than humans, leading to better outcomes.
- Greater Adaptability and Responsiveness: Agentic AI's capacity to learn and adapt to dynamic environments means it can respond to unforeseen situations, changing conditions, or new information with agility, maintaining effectiveness even in uncertain scenarios.
- Personalization at Scale: By understanding user preferences and historical interactions, Agentic AI can deliver highly personalized experiences and services, from tailored product recommendations to customized customer support.
- Human Augmentation: Rather than replacing humans, Agentic AI often serves as a powerful augmenter, enhancing human capabilities and productivity by taking on routine, tedious, or data-intensive tasks. This allows human professionals to leverage their unique skills more effectively.
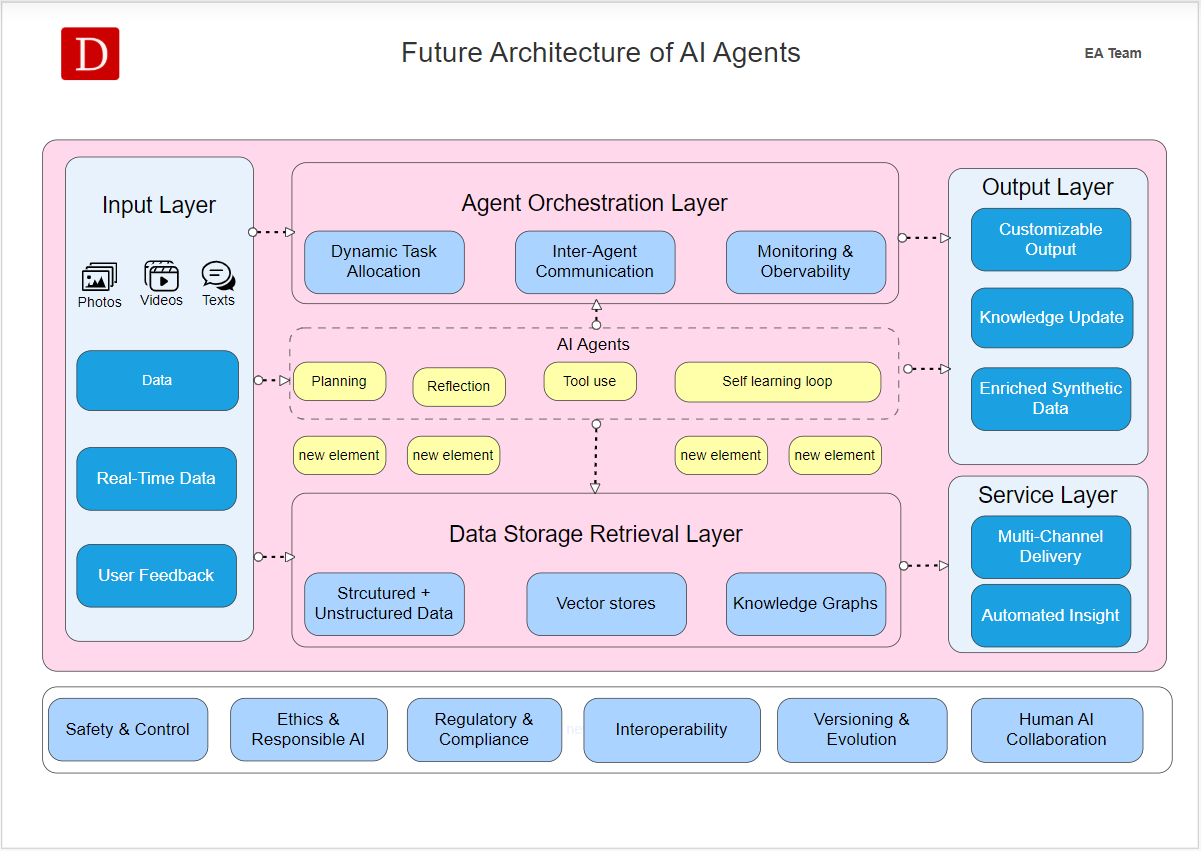
Future Architecture of AI Agents.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Agentic AI is poised to transform various sectors, with early applications already demonstrating its potential
- Customer Service and Support
- Autonomous Customer Journey Managers: AI agents can guide customers through complex issues, provide personalized support, resolve problems autonomously, and even proactively offer solutions based on predictive analysis, reducing the need for human intervention in routine cases.
- Proactive Support: Identifying potential issues before they arise (e.g., detecting a service interruption) and proactively notifying customers or initiating a fix.
- IT Operations and Cybersecurity
- Automated IT Troubleshooting: AI agents can diagnose and resolve common IT issues (e.g., password resets, software installations, network problems) by analyzing system logs and knowledge bases, and even executing fixes.
- Real-time Threat Detection and Response: In cybersecurity, agentic AI can continuously monitor network traffic, detect anomalies, prioritize risks, and even initiate automated response actions to neutralize threats, significantly reducing response times.
- Business Process Automation and Optimization
- Workflow Orchestration: Managing and coordinating complex, multi-step business processes across different systems and departments, such as supply chain management, financial operations, or human resources.
- Intelligent Data Analysis: Continuously analyzing large datasets to surface insights, predict trends, and identify opportunities or bottlenecks, aiding strategic decision-making.
- Healthcare
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Analyzing patient data to recommend tailored treatments and adjust them dynamically based on new test results.
- Drug Discovery: Accelerating the identification of potential drug candidates by analyzing vast biological and chemical datasets.
- Autonomous Systems
- Self-Driving Vehicles: Agentic AI is at the heart of autonomous vehicles, processing real-time sensor data, planning routes, making driving decisions, and adapting to dynamic road conditions to ensure safe navigation.
- Robotics: Enabling robots to perform complex tasks in unstructured environments, such as manufacturing, logistics, or even exploration, by perceiving, planning, and executing actions autonomously.
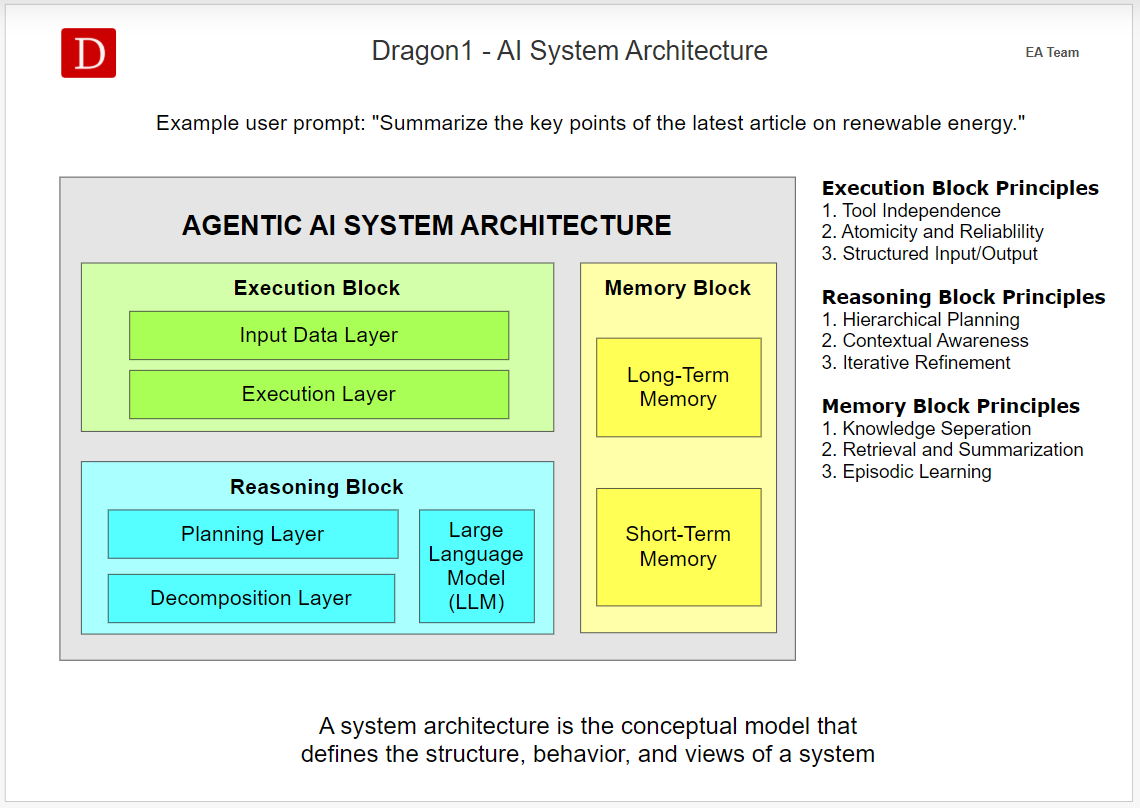
Agentic AI System Architecture.
Agentic AI Quiz
1. What is the primary characteristic that differentiates Agentic AI from traditional AI systems?
A) Autonomy: Agentic AI systems are designed to operate independently and make decisions without constant human oversight.
B) Data processing speed: While important, it's not the defining characteristic of agentic AI.
C) Large language model integration: Many agentic AIs use LLMs, but it's a component, not the core differentiator.
D) Ability to perform simple automation: Traditional AI can also do this; agentic AI goes beyond.
2. Which of the following is NOT a core principle of Agentic AI architecture?
A) Adaptability: Agentic AI should be able to adjust its behavior based on new data or environmental changes.
B) Goal-Oriented Behavior: Agentic AI operates with specific objectives in mind.
C) Continuous Learning: Agentic AI systems are designed to learn and improve over time.
D) Static Functionality: Agentic AI is dynamic and evolves, not static.
3. What role does the 'Perception Module' play in an Agentic AI system?
A) It executes actions in the environment.
B) It stores long-term memories.
C) It gathers and interprets data from the environment: This module allows the AI to 'see' and 'hear' its surroundings.
D) It plans future actions.
4. How does Agentic AI typically handle complex, multi-step problems?
A) It requires human intervention at each step.
B) It only performs single, predefined actions.
C) It breaks down goals into sub-tasks and pursues them independently, often coordinating multiple agents and tools: This allows for dynamic and complex problem-solving.
D) It relies solely on a single large language model for all tasks.
5. Which of these describes 'Reinforcement Learning' in the context of Agentic AI?
A) Learning from labeled datasets.
B) Learning through trial and error by receiving feedback (rewards or penalties) based on actions: This allows the AI to refine its strategies.
C) Learning by exploring unlabeled data.
D) Learning from human demonstrations.
6. What is a key benefit of 'Modularity' in Agentic AI architecture?
A) It simplifies the perception module.
B) It allows components to be developed, tested, and updated independently, enhancing scalability and integration. This makes the system more robust and easier to manage.
C) It limits the AI's ability to learn.
D) It prevents the AI from interacting with external tools.
7. In an Agentic AI system, what is the purpose of the 'Cognitive Module'?
A) To physically interact with the environment.
B) To store raw sensory data.
C) To process information, set goals, devise plans, and make decisions: This is essentially the 'brain' of the AI.
D) To manage communication between different AI systems.
8. How does Agentic AI differ from generative AI?
A) Generative AI focuses on acting, while Agentic AI focuses on creating content.
B) Generative AI focuses on creating content, while Agentic AI focuses on planning, deciding, and executing to reach outcomes: Agentic AI builds on generative capabilities by applying outputs toward specific goals.
C) They are synonymous terms.
D) Agentic AI does not use generative AI at all.
9. What does 'Proactiveness' mean in the context of Agentic AI?
A) The AI only acts when explicitly triggered by a human.
B) The AI can identify needs or opportunities and initiate actions without explicit prompts: It doesn't wait for instructions.
C) The AI always asks for human confirmation before acting.
D) The AI performs tasks at a predefined schedule.
10. What is a 'multi-agent system' (MAS) architecture in Agentic AI?
A) A system where a single agent handles all tasks sequentially.
B) A system where multiple independent AI agents collaborate or compete to achieve common or individual objectives: This allows for
tackling more complex tasks.
C) A system that only performs reactive actions.
D) A system that requires constant human supervision for coordination.
As Agentic AI continues to evolve, its ability to reason, adapt, and act independently will unlock even more sophisticated applications, driving a new era of intelligent automation and human-AI collaboration. Understanding these foundational concepts is key to navigating this exciting frontier.
Read all about Generative Artificial Intelligence Examples [PDF] and sign up here for your Free Trial Account.